Many LED lightings come with dimmable functions, allowing you to adjust brightness. There are many methods out there you can use to dim your LED strips. The size of your lighting project determines the one you’ll choose. Small projects use TRIAC and PMWs, while larger ones use DALI, 0-10V or DMX methods.
In this post, we’ll provide you with the know-how so you can choose the best dimming option for your specific application.
- Benefits of Dimming LED Strip Lights
Dimmable lighting gives you the option to match the lighting to your particular activity. You may want a bright light as task lighting, but a dim, relaxing light during evening dines.
Dimming also sees extensive use within commercial and industrial spaces. For example, dimmable lighting offers flexibility to your office space. It allows for optimal lighting that suits your employees’ needs.
1. Are all LED Strips Dimmable?
Basically, all the strip lightings are dimmable, the brightness can be adjusted by providing a compatible DC signal.
You may see a “NOT DIMMABLE” label listed on the LED bulb, this is because their internal electrical circuitry doesn’t interpret the wall dimmer signal. Which works for traditional incandescent bulbs only. LED strips don’t connect directly to 120V/220V AC wall sockets. They need a power supply to convert AC into lower 12V or 24V DC voltage.
So, If a wall dimmer is involved, it must first “communicate” to the power supply before any dimming can happen at the LED strip. The “dimmable/not dimmable” question depends on if the power supply can interpret the dimming signal produced by the wall dimmer.
2. Factors to Consider When selecting a Dimming Method
Let’s go over two of the main factors you’ll need to consider when choosing a dimming option.
Your Project’s Size
If you have a sizable project, such as those with more than a dozen strip reels, you’ll need DALI, 0-10v, and DMX LED dimmers. These dimmers can manage multiple zones.
For small projects that consist of just a single power supply, you’ll need the simpler TRIAC and PWM dimming.
The Type of Dimmer Interface You Prefer
There are many types of dimmer interfaces that you can use for your strips. Available interfaces include touchscreens, rotaries, wifi functions, and more.
Say you want to opt for a wireless touch-sensitive dimmer. In that case, you can skip any type of dimmer that involves wires.
3. Dimming for Small Projects.
Here, we’ll dive into details on dimming options available for small-scale projects.
3.1 Triac Dimming
Most wall dimmers available today use the TRIAC dimming signal. You’ll need to find a dimmable power supply for these wall dimmers.
The TRIAC dimmable power supply has two functions:
- Change 120V/220V AC to 12/24V DC signal for led strip lights.
- Interpret dimming signals produced by the Triac wall dimmer and then translate that into the LED strip’s output.
You’ll need to connect the TRIAC dimmer to the dimmable power supply, then link the power supply’s output to the LED strip.
To avoid voltage drops, ensure that your power unit stays close to your strip lights. Here are the two types of triac dimming options.
- Traditional AC triac dimming:
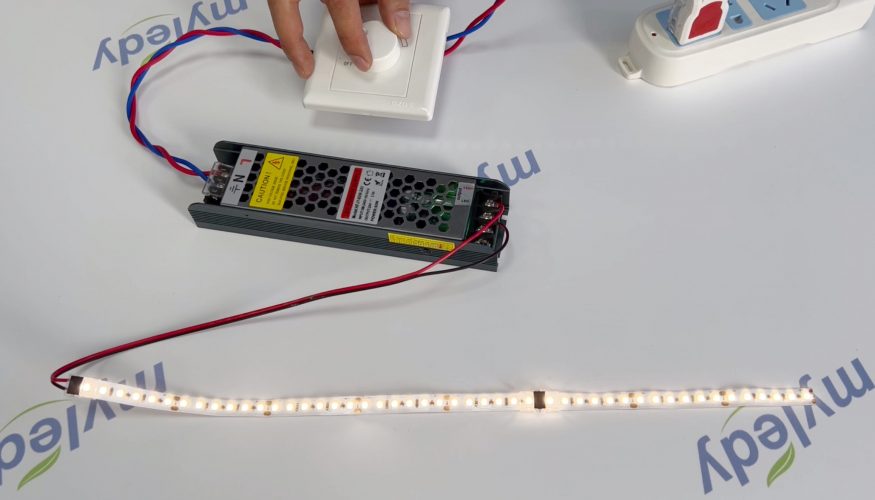

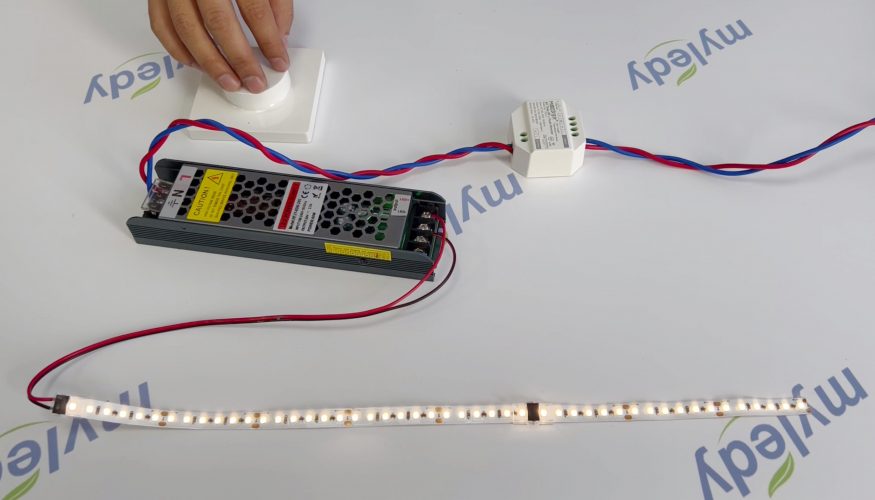
- Modern AC triac RF dimming:

3.2 Low-Voltage PWM Dimming
PWM, or “pulse width modulation” is a dimming method used for many LED strip applications. PMW is a digital signal that “talks” to your strip’s power supply to adjust brightness. You can install a DC PWM dimmer between a standard, non dimmable power supply and the LED strip. It usually has a turn dial (potentiometer) that adjusts the LED strip brightness. The power supply can be any standard DC power unit and does not need to be dimmable.
Compared to TRIAC dimmable power supplies, these cost cheaper and are readily available. This simple circuit design works well for portable installations where you don’t have to build a dimmer into a wall. DC PWM dimmers are very simple to assemble, easily connecting to the power supply and LED strip.
There are different PWM dimmers available:
Inline Knob Dimming
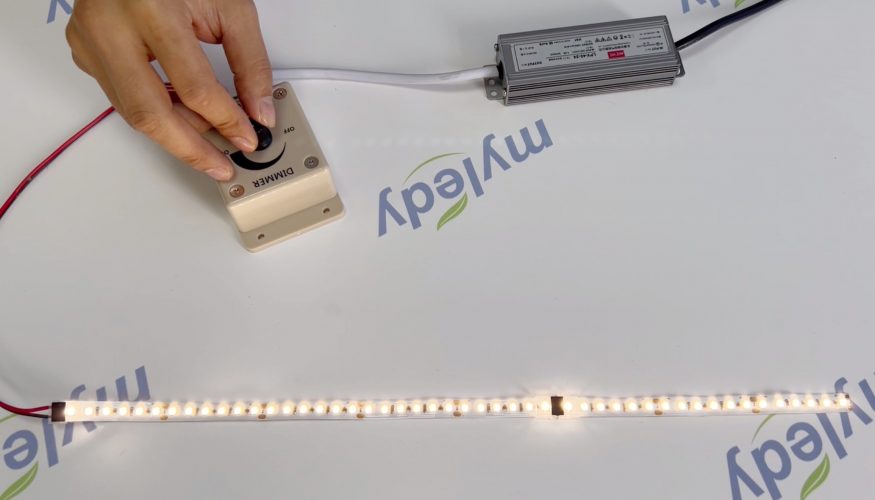

Inline LED dimmers involve wires that run directly from the power unit to your strip lights. Because of this standalone capability, it’s only applicable for smaller-scale lighting projects.
RF Dimming
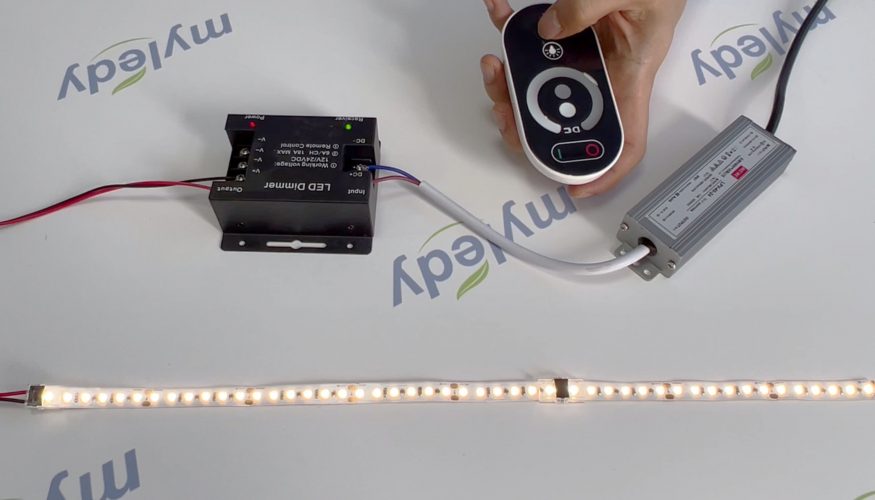

RF or “radio frequency” dimming provides a remote way to adjust your strip brightness.
Unlike the wired inline LED dimmers, you can dim the led strip by remote control, the distance can get as far as 20 meters in diameter.
WIFI Dimming
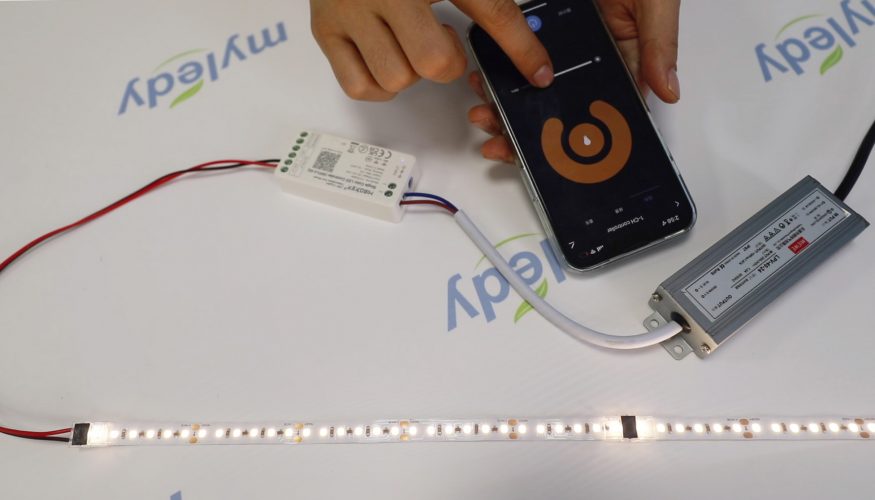

A smart dimmer allows you to control your LEDs remotely via a WiFi connection. When setting up a “smart” home or office lighting system, these dimmers are necessary.
You can operate the dimming by using a mobile app. This feature lets you adjust brightness using Alexa or Google Assistant voice controls.
4. Dimming for Large Projects
The following dimming techniques suit larger-scale projects. Your lighting system may have many reels and power units, like those used in commercial areas.
4.1 0/1-10V Dimming
0-10V dimming lets you adjust brightness by altering DC voltage powering your strips.
It can vary voltage between zero and ten volts – zero being “off” and ten at 100% brightness output.
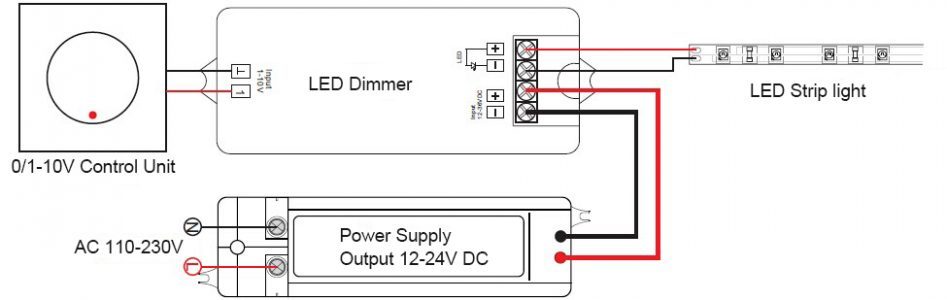
This method lets you link as many dimming receivers as your project requires. This means you’ll be able to manipulate many dimmable LED lights simultaneously.
4.2 DALI Dimming
DALI dimming is a step further from the 0-10V system. Like the 0-10V, this dimmer allows you to adjust many LED strips over a wide area using a central controller.
This method also allows individual users to adjust brightness for specific zones using smaller LED dimmers.
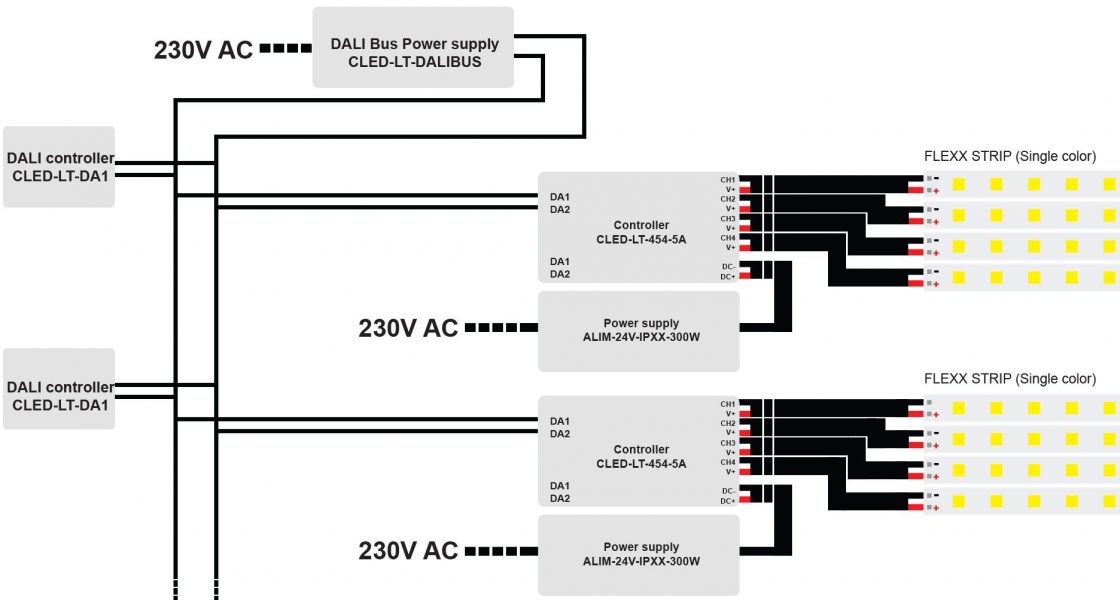
This setup makes for a convenient way to adjust brightness without going all the way to the main switch. Like its 0-10V predecessor, you’ll have to wire it between the dimmable strips and the transformer.
4.3 DMX Dimming
“DMX 512” also works by regulating voltage in the transformer to reduce brightness.
Despite being an old dimming method, DMX is still used today. Applications include large-scale installations, such as concerts, theatre, and other performance venue lighting. This method allows for independent control of different areas of the lighting project. It can run up to 512 DMX receivers, also called channels.
There are two ways to wire this dimming system: daisy-chaining and splitting.
- The Daisy Chain method requires connecting the wires of each fixture from a loop of the previous one. By wiring this way, you’ll get a line of fixtures that connects to the receiver, decoder, and console of the DMX system. It has a limitation, though. You won’t connect more than 32 fixtures in one chain. Going over this limit will hinder the signal strength required for DMX communication.
- DMX splitting is needed if you need to connect more than 32 fixtures. Splitting allows you to expand the communication network by duplicating the DMX output many times.
5. LED Dimming FAQs
What’s the Difference Between an LED Controller and Dimmer?

Regarding LED lighting systems, you may be confused about the terms “controller” and “dimmer.” Simply put, both terms mean the same thing. Both devices allow you to manipulate the settings and brightness of your installation.
Many lighting manufacturers use “LED dimmers” to refer to control units for single-colored LED reels. These control units let you switch on/off your LED lights and adjust their light level.
On the other hand, the term “LED controller” often refers to control units that manage RGB or color-changing LED strips. These devices have more functions than a single-color dimmer. Apart from dimming your strips, you can use them to put up color scrolls and time delays. They also allow you to strobe, color mix, and do many other customizations.
Why Do LEDs Flicker When Dimmed?
There are instances when LEDs may flicker when you try to dim them. The leading cause of this flickering is voltage fluctuations from surge wattage.
Surge wattage occurs when you turn on other electrical appliances in your home. The wirings on these appliances create a resistance in the home’s electricity. This sudden change causes a voltage drop in your LED lights.
Surge wattage dimming becomes noticeable when you set your LEDs on low brightness. If your brightness is too high, you’ll rarely experience flickering.
Why Do LEDs Flicker on Video?
You may have noticed that your LED lights flicker when on camera or video.
To get to the bottom of this, we need to understand that LEDs actually blink in real-time. But it happens so fast that your eyes can’t see the flickering.
When you record on video, flickering becomes evident due to the “strobe effect.” The strobe effect occurs because your camera’s frames per second do not level with electricity’s frequency.
Will Dimming Reduce the Tape’s Service Life?
Dimming doesn’t generally affect the lifespan of LEDs. Reducing an LED light’s brightness will produce less heat. Reduced heat is always suitable for your LED’s internal components.
For that reason, having a constant low brightness may even prolong your LEDs’ lifespan.
Do Dimmers Save Electricity?
Energy-saving qualities depend on which type of dimmer you use. Older dimmers consume the same power amount despite producing decreased brightness. In this case, that extra unused energy converts to heat instead.
Modern dimmers can provide electricity savings. They have the technology to only send the amount of energy your LED needs based on brightness.
The Last Words
Choosing a right dimmer can bring much convenience to the control of our lighting system. We can adjust the brightness of the light according to the external light and specific needs. In addition, Dim-to-Warm LED strip light can also adjust the color temperature to meet different occasions.
Ready to get your lighting project going? We have a fantastic selection of state-of-the-art dimmable LED strip lights. Browse our high-quality selection here on Myledy!














